Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle: What Each Phase Means
Understanding your menstrual cycle is one of the most powerful tools for managing your reproductive health. Whether your goal is to track your cycle, plan or avoid pregnancy, or simply understand what your body is communicating, knowing how each phase works can help you make informed decisions.
The menstrual cycle is more than just a monthly period. It is a continuous process involving hormones, physical changes, emotional shifts, and fertility signals. By learning how to track your cycle and recognize each phase, you gain control, awareness, and confidence in your body.
This article explains the menstrual cycle in a clear, practical way and shows how cycle tracking and pregnancy tracking apply during:
-
Normal cycles
-
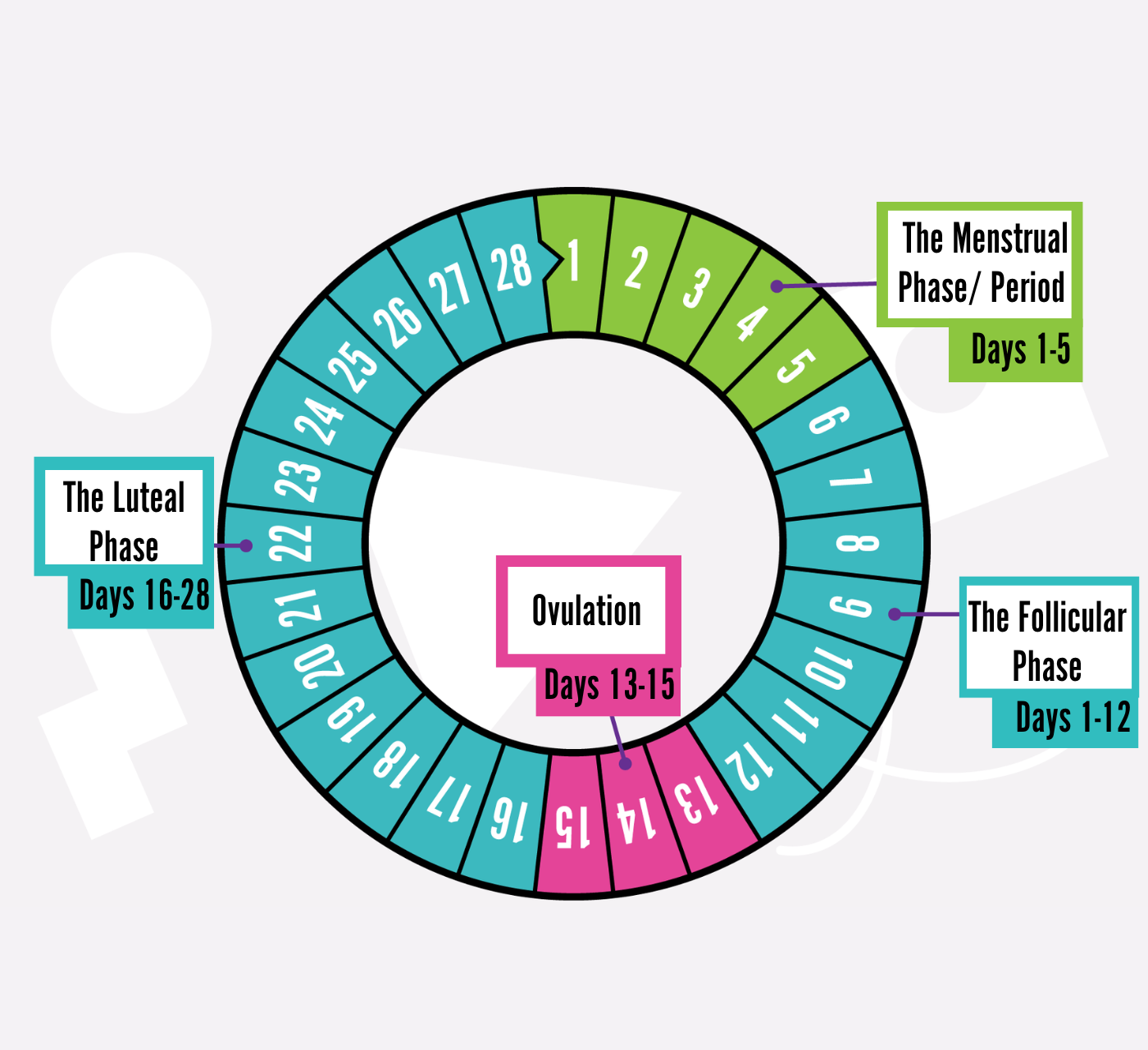
Menstrual phase
-
Follicular phase
-
Ovulation phase
-
Luteal phase
-
Late periods
Track Cycle: Why Understanding Your Cycle Matters
Cycle tracking involves observing and recording changes in your body over time. This can be done through a website or mobile app and helps you understand:
-
When your period is expected
-
When you are most fertile
-
How hormones affect your mood and energy
-
Whether your cycle is regular or irregular
-
Early signs of pregnancy or hormonal imbalance
A “normal” menstrual cycle typically lasts between 21 and 35 days, but normal varies from person to person. Tracking your cycle over several months helps define what “normal” means for you.
Cycle tracking is useful for:
-
Menstrual health awareness
-
Pregnancy planning
-
Pregnancy prevention
-
Identifying late or missed periods
-
Communicating better with healthcare providers
Track Pregnancy: How Cycle Phases Connect to Fertility
Pregnancy can only occur during a specific window of the menstrual cycle—around ovulation. Tracking your cycle allows you to:
-
Identify fertile days
-
Increase chances of conception
-
Recognize early pregnancy symptoms
-
Detect unusual cycle changes
Missed or late periods, combined with symptoms like breast tenderness, fatigue, or nausea, can signal pregnancy. That’s why understanding each phase is essential.
Normal Cycle: What a Healthy Cycle Looks Like
A normal cycle follows a predictable pattern, even if the length differs slightly each month. Signs of a healthy cycle include:
-
Periods arriving within a consistent range
-
Bleeding lasting 3–7 days
-
Manageable cramps or discomfort
-
Clear signs of ovulation
-
Stable energy changes across phases
Tracking a normal cycle helps you quickly notice changes such as:
-
Late periods
-
Missed ovulation
-
Short or long cycles
-
Hormonal irregularities
Consistency over time matters more than perfection.
Menstrual Phase: The Start of the Cycle
What it is:
The menstrual phase begins on the first day of bleeding. This marks the start of a new cycle.
What happens in the body:
-
The uterus sheds its lining
-
Hormone levels (estrogen and progesterone) are low
-
Menstrual blood flows for several days
Common experiences:
-
Bleeding
-
Cramps
-
Fatigue
-
Lower energy
-
Emotional sensitivity
Cycle tracking during this phase:
-
Record the start date and length of bleeding
-
Note flow intensity (light, medium, heavy)
-
Track pain, mood, and energy
Pregnancy tracking relevance:
-
Pregnancy is unlikely during this phase
-
Bleeding usually indicates that pregnancy has not occurred
-
However, light bleeding can sometimes be confused with implantation bleeding, so tracking patterns matters
Follicular Phase: Preparing for Ovulation
What it is:
The follicular phase starts after menstruation and lasts until ovulation.
What happens in the body:
-
The brain signals the ovaries to prepare eggs
-
Estrogen levels begin to rise
-
The uterine lining thickens
-
One egg matures
Common experiences:
-
Increased energy
-
Improved focus
-
Better mood
-
Clearer thinking
-
Light vaginal discharge
Cycle tracking during this phase:
-
Track changes in energy and mood
-
Observe cervical mucus becoming lighter or sticky
-
Monitor cycle length consistency
Pregnancy tracking relevance:
-
Pregnancy is still unlikely early in this phase
-
Fertility gradually increases as ovulation approaches
-
Important preparation phase for conception
Ovulation Phase: Peak Fertility Window
What it is:
Ovulation occurs when the ovary releases a mature egg. This egg survives for about 12–24 hours, but sperm can live up to 5 days.
What happens in the body:
-
Estrogen peaks
-
Luteinizing hormone triggers egg release
-
The egg travels toward the uterus
Common signs of ovulation:
-
Clear, stretchy cervical mucus (like egg whites)
-
Mild lower abdominal pain
-
Increased libido
-
Heightened senses
-
Slight temperature rise after ovulation
Cycle tracking during this phase:
-
Mark ovulation day
-
Track fertile window (5 days before ovulation + ovulation day)
-
Use symptoms or app predictions
Pregnancy tracking relevance:
-
This is the only time pregnancy can occur
-
Unprotected sex during this window may lead to conception
-
Planned intercourse increases pregnancy chances
Luteal Phase: Post-Ovulation Changes
What it is:
The luteal phase begins after ovulation and lasts until the next period.
What happens in the body:
-
Progesterone increases
-
The uterus prepares for possible pregnancy
-
If no pregnancy occurs, hormones drop
Common experiences:
-
Calmer energy
-
Increased appetite
-
Breast tenderness
-
Mild bloating
-
PMS symptoms in some people
Cycle tracking during this phase:
-
Track mood and physical symptoms
-
Note luteal phase length (usually 12–14 days)
-
Watch for unusual spotting
Pregnancy tracking relevance:
-
If pregnancy occurs, progesterone remains high
-
Early pregnancy symptoms may appear
-
Implantation usually happens in this phase
Late Period: What It Can Mean
A late period is when menstruation does not arrive on the expected day.
Common causes of a late period:
-
Pregnancy
-
Stress
-
Hormonal imbalance
-
Travel or lifestyle changes
-
Illness
-
Irregular ovulation
Cycle tracking during a late period:
-
Check how many days late
-
Review ovulation timing
-
Track symptoms like nausea, fatigue, or breast changes
Pregnancy tracking relevance:
-
A late period is often the first sign of pregnancy
-
Pregnancy tests are most accurate after a missed period
-
Continued tracking helps confirm patterns
Why Cycle & Pregnancy Tracking Work Best Together
Tracking both your cycle and pregnancy-related signs allows you to:
-
Understand fertility windows
-
Plan pregnancy naturally
-
Identify irregular cycles early
-
Improve reproductive health awareness
-
Make informed healthcare decisions
Using a website or mobile app makes tracking easier by:
-
Predicting phases
-
Storing long-term data
-
Sending reminders
-
Visualizing patterns
Final Thoughts
Your menstrual cycle is a monthly health report from your body. Each phase—from menstruation to ovulation to the luteal phase—serves a purpose. When you track your cycle consistently, you gain insight into your fertility, hormonal balance, and overall well-being.
Whether you are tracking for health, pregnancy planning, or general awareness, understanding what each phase means empowers you to work with your body, not against it.
Related Articles
Understanding Fertility Windows and Planning for Conception
Understanding Early Pregnancy Changes

Common Cycle Changes and When to Worry
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle and Tracking Your Period
How Lifestyle Affects Your Menstrual Cycle
Understanding Timing, Accuracy, and Results

What Happens in Your Body During Menstruation

Understanding Your Baby’s Timeline