Common Cycle Changes and When to Worry

Menstrual cycles are not static. It is normal for your cycle to change over time due to lifestyle, age, stress, and health factors. While some changes are harmless and temporary, others may signal that something needs attention. Understanding common cycle changes—and knowing when to worry—helps you protect your reproductive health and use cycle and pregnancy tracking tools more effectively.
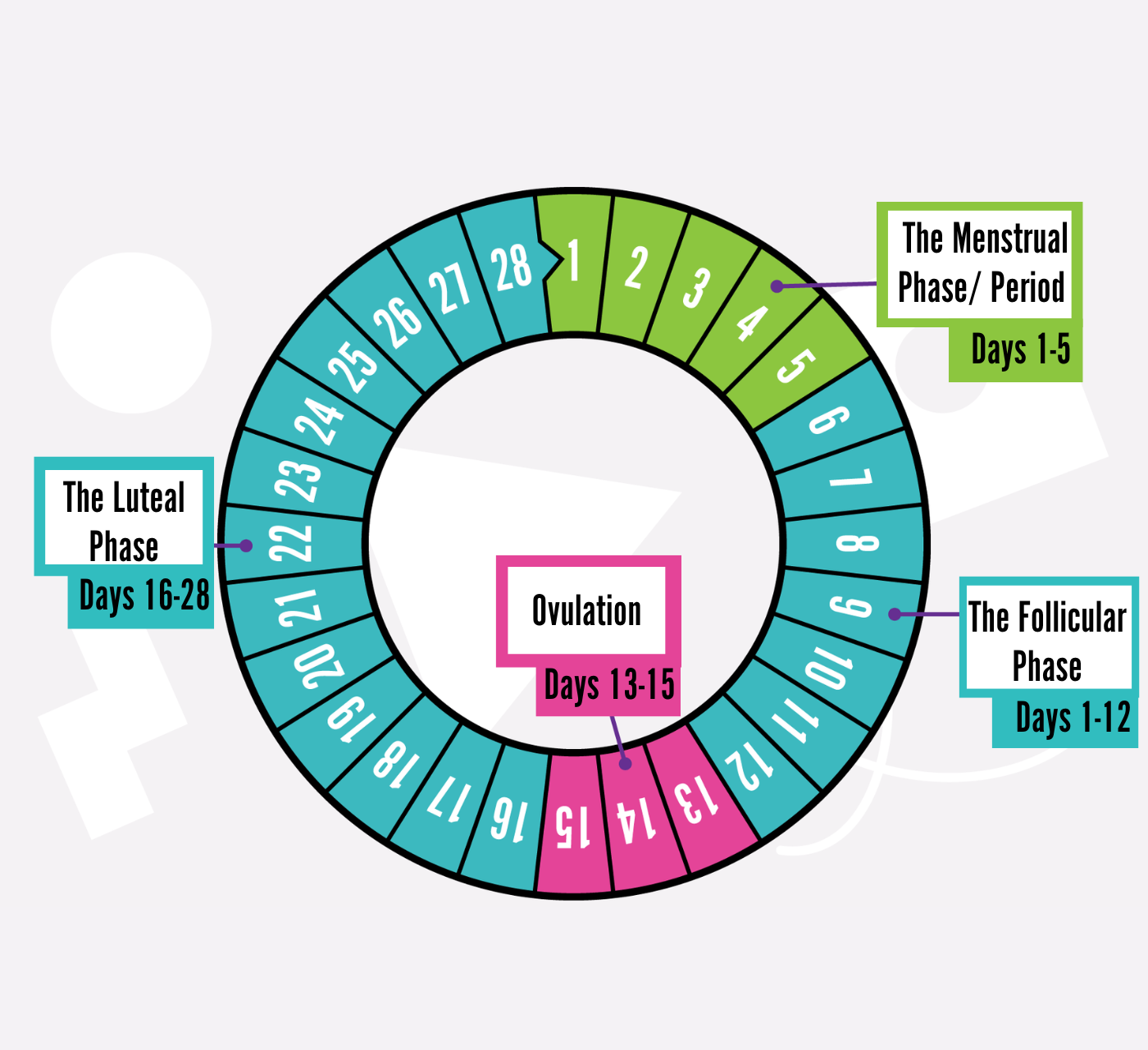
By tracking your cycle across all phases—normal, menstrual, follicular, ovulation, luteal, and late period—you can identify patterns, spot irregularities early, and decide when professional advice may be needed.
Track Cycle: Why Changes Matter
Tracking your menstrual cycle over time allows you to recognize what is normal for your body and what is not. Small variations from month to month are expected, but consistent or sudden changes may indicate hormonal shifts or health concerns.
Cycle tracking helps you:
-
Notice changes in cycle length
-
Identify missed or delayed ovulation
-
Track symptom intensity
-
Monitor bleeding patterns
-
Detect early warning signs
A website or mobile cycle tracker organizes this information, making trends easier to see than relying on memory alone.
Track Pregnancy: Understanding Changes Related to Fertility
Many cycle changes are closely linked to fertility and pregnancy. Changes in ovulation timing, luteal phase length, or period timing can affect the chances of conception.
Pregnancy-related tracking helps you:
-
Understand late or missed periods
-
Recognize early pregnancy symptoms
-
Differentiate between cycle delays and conception
-
Avoid unnecessary worry
Knowing which changes are common and which are concerning helps you respond calmly and accurately.
Normal Cycle: Expected Variations vs. Red Flags
Even in healthy individuals, cycles can vary slightly.
Common, normal changes include:
-
Period arriving a few days earlier or later
-
Slight changes in flow
-
Minor shifts in cycle length
-
Temporary PMS differences
Changes that may need attention:
-
Cycle length consistently shorter than 21 days or longer than 35 days
-
Sudden major changes in timing
-
Periods disappearing for several months
-
Frequent irregular cycles
Tracking your cycle for several months helps distinguish between normal variation and patterns that may require follow-up.
Pregnancy relevance:
Unexpected changes in a previously regular cycle may indicate pregnancy or delayed ovulation.
Menstrual Phase: Changes in Bleeding Patterns
Changes in your period are often the most noticeable.
Common and usually normal changes:
-
Slightly heavier or lighter flow
-
Shorter or longer bleeding by a day
-
Color changes from bright red to dark brown
-
Mild clotting
When to worry:
-
Extremely heavy bleeding (soaking pads/tampons very frequently)
-
Periods lasting longer than 7 days
-
Severe pain that interferes with daily activities
-
Bleeding between periods
What to track:
-
Flow intensity
-
Duration
-
Pain levels
-
Unusual spotting
Pregnancy relevance:
Light bleeding can sometimes be confused with implantation bleeding. Tracking helps differentiate normal periods from pregnancy-related spotting.
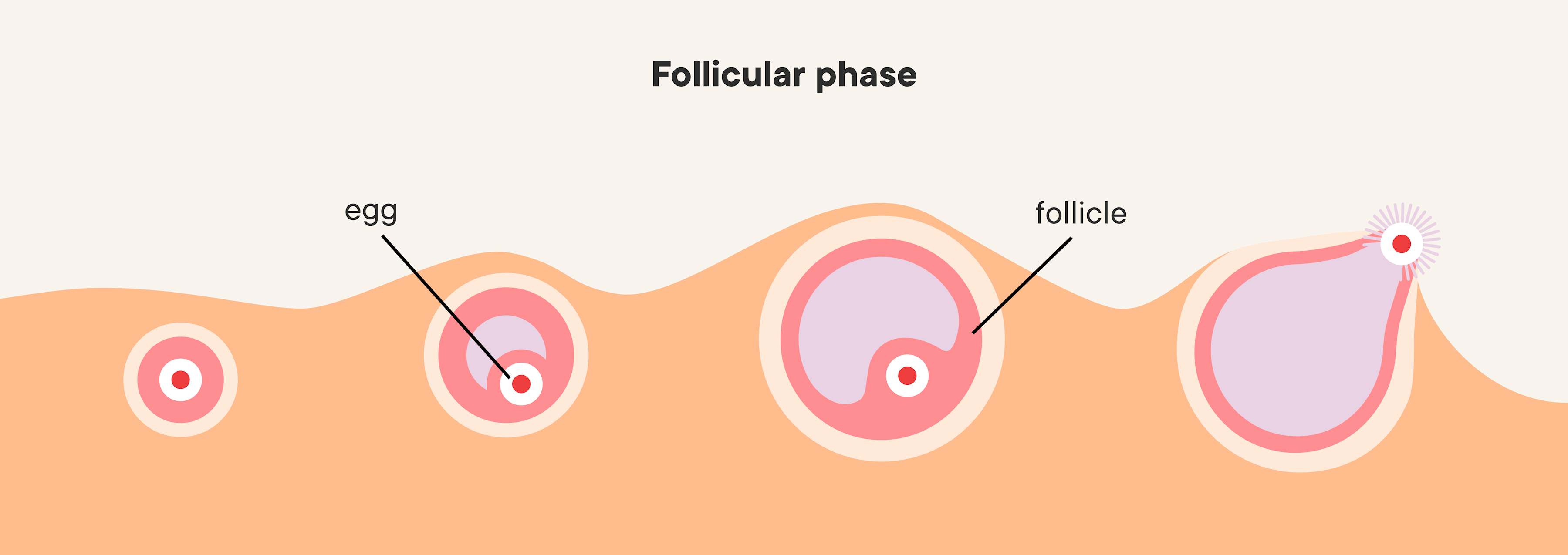
Follicular Phase: Energy and Hormonal Changes
The follicular phase reflects how your body prepares for ovulation.
Common, normal changes:
-
Gradual energy increase
-
Mood improvement
-
Clear thinking
-
Mild fluctuations in focus
When to worry:
-
Extremely low energy throughout the phase
-
No noticeable shift after menstruation
-
Repeated lack of ovulation signs
These may indicate hormonal imbalance or delayed ovulation.
Pregnancy relevance:
An unhealthy follicular phase may affect ovulation timing and fertility.
Ovulation Phase: Changes in Fertility Signs
Ovulation is a key indicator of cycle health.
Normal ovulation changes:
-
Clear, stretchy cervical mucus
-
Mild pelvic discomfort
-
Increased libido
-
Slight bloating
When to worry:
-
No ovulation signs for multiple cycles
-
Ovulation occurring very early or very late consistently
-
Severe ovulation pain
-
Fertile window disappearing suddenly
Missing ovulation occasionally can be normal, but repeated absence should be monitored.
Pregnancy relevance:
Without ovulation, pregnancy cannot occur. Accurate tracking helps identify ovulation issues early.
Luteal Phase: Mood and Symptom Changes
The luteal phase supports potential pregnancy.
Common, normal changes:
-
Slight mood sensitivity
-
Increased appetite
-
Mild breast tenderness
-
Lower energy near period start
When to worry:
-
Luteal phase shorter than 10 days consistently
-
Severe PMS symptoms
-
Sudden intense mood changes
-
Significant sleep disruption
These may suggest low progesterone or hormonal imbalance.
Pregnancy relevance:
A healthy luteal phase supports implantation and early pregnancy.
Late Period: When Delays Are Normal—and When They’re Not
A late period can cause concern, but it is not always serious.
Common reasons for a late period:
-
Stress
-
Travel
-
Lifestyle changes
-
Delayed ovulation
-
Illness
When to worry:
-
Period is more than a week late repeatedly
-
Late periods occur frequently
-
Late period with severe symptoms
-
Negative pregnancy test but no period for weeks
Tracking ovulation helps determine whether the delay is due to late ovulation or another cause.
Pregnancy relevance:
Late periods are often the first sign of pregnancy. Consistent tracking improves interpretation.
Patterns That Deserve Extra Attention
While single-cycle changes are often harmless, patterns matter.
Watch closely if you notice:
-
Increasing irregularity over time
-
Persistent cycle shortening or lengthening
-
Frequent missed periods
-
Sudden symptom intensity changes
A cycle tracker helps visualize these patterns clearly.
How Cycle Tracking Helps You Decide When to Worry
Accurate tracking helps you:
-
Compare cycles objectively
-
Avoid unnecessary anxiety
-
Recognize meaningful changes early
-
Provide clear information to healthcare providers
Data from a cycle tracker can be more useful than memory alone when seeking advice.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consider professional guidance if:
-
Changes persist for 3 or more cycles
-
Bleeding or pain is severe
-
Periods stop for several months
-
Pregnancy is suspected but unclear
-
Cycle changes affect daily life
Tracking gives you valuable information to share during consultations.
Why Cycle & Pregnancy Tracking Work Best Together
Cycle changes often affect fertility and pregnancy timing. Tracking both together provides:
-
Clear fertility windows
-
Better pregnancy awareness
-
Early detection of irregularities
-
Greater confidence in reproductive health decisions
Final Thoughts
Cycle changes are a natural part of life, and many are completely normal. The key is understanding your own patterns and recognizing when changes are temporary versus persistent.
By tracking your cycle and pregnancy signs consistently, you empower yourself to notice what your body is telling you. Awareness—not fear—is the goal. With the right tracking tools and knowledge, you can respond to changes calmly and confidently.
Related Articles
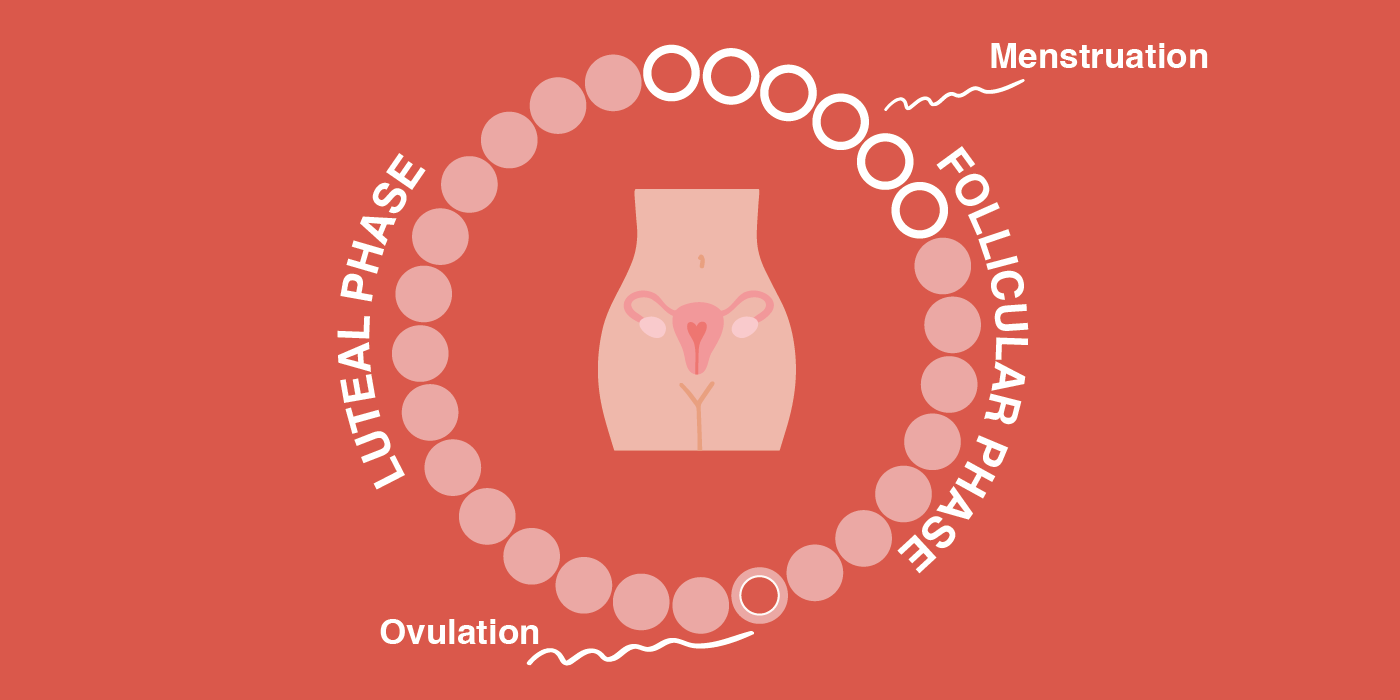
What a Healthy Menstrual Cycle Looks Like

Understanding Your Baby’s Timeline
How Lifestyle Affects Your Menstrual Cycle
Understanding Timing, Accuracy, and Results
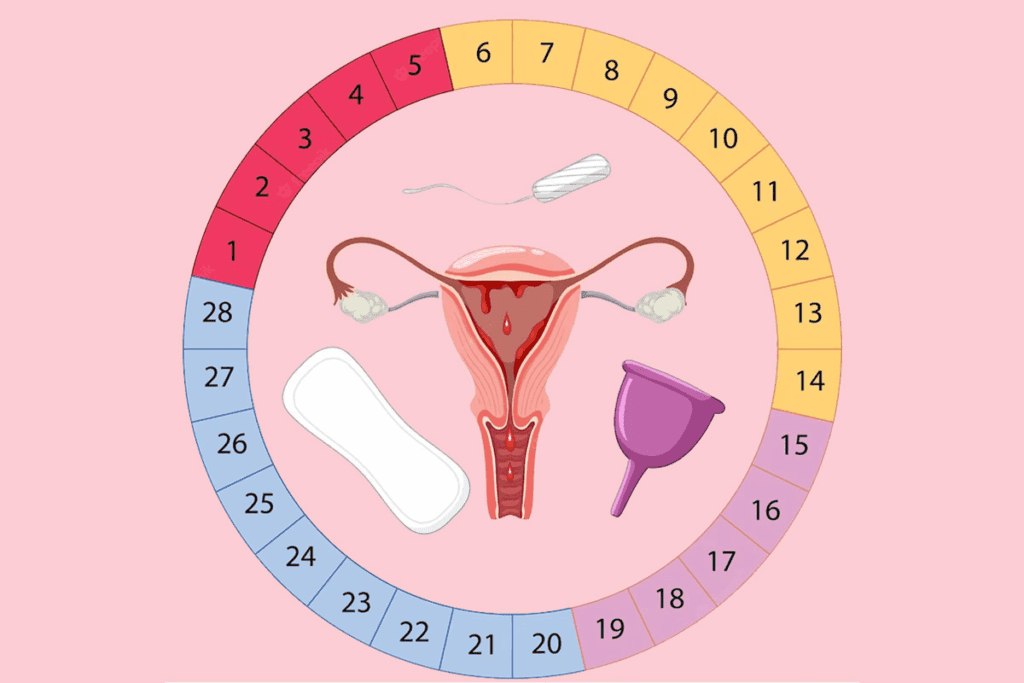
How to Track Your Period Accurately Using a Cycle Tracker
Understanding Fertility Windows and Planning for Conception
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle and Tracking Your Period
Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle: What Each Phase Means